Buying Overhead Cranes for Steel Fabrication in Qatar
Buying Overhead Cranes for Steel Structure Fabrication in Al Daayen, Al Wakrah & Doha
For steel structure fabrication workshops in Al Daayen, Al Wakrah, and Doha, the right overhead crane is not defined by tonnage alone—it is defined by how well the crane matches your workshop layout, steel component size, lifting frequency, corrosion environment, and long-term expansion plans. Check types of industrial cranes for sale in Qatar or leave us a message to get your tailored design.
Choosing the wrong crane leads to wasted capital, workflow bottlenecks, and premature maintenance issues in Qatar’s demanding industrial conditions.
Key Takeaways
- Not all steel fabrication overhead cranes are designed for Qatar’s wide workshops and heavy fabricated steel members
- Span, lift height, duty class, and crane runway design matter more than nominal capacity
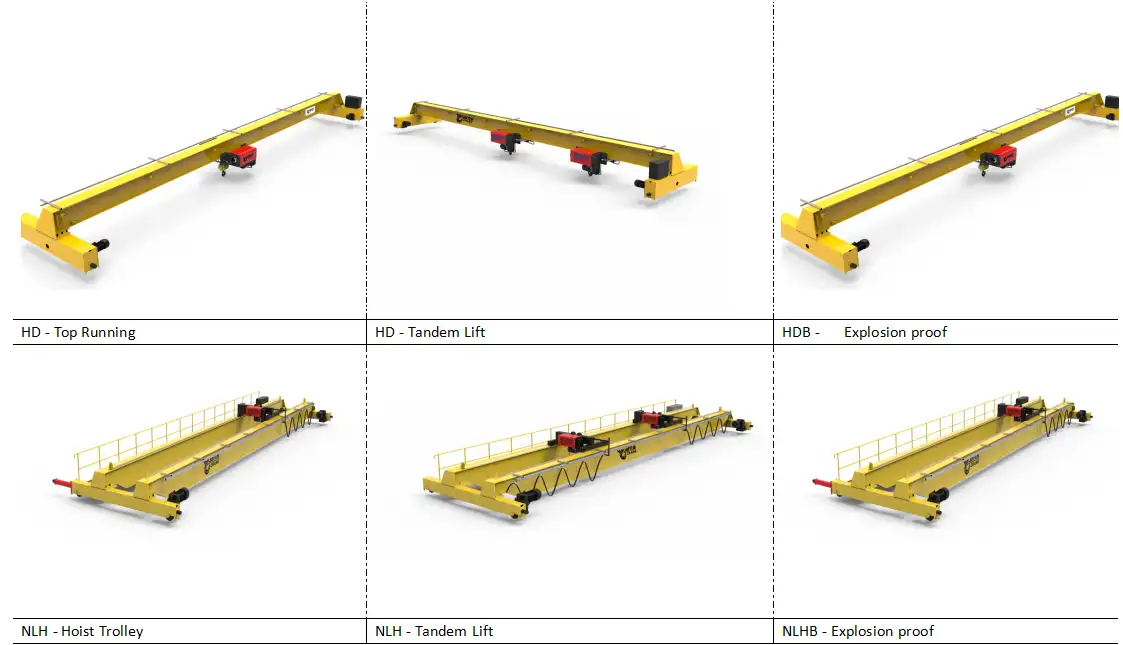
- Double girder overhead cranes dominate steel structure workshops for stability and hook coverage
- Corrosion protection and electrical compliance are critical in Doha, Al Wakrah, and coastal zones
- Buyers should evaluate total lifecycle cost, not just crane price
- Proper selection reduces rework, downtime, and safety risks
Frequently Asked Questions: Steel Fabrication Cranes in Qatar
Q1: What types of steel materials are commonly handled in Qatar's fabrication workshops?
- Structural steel beams and H-sections: Long, narrow pieces needing stability during lifting.
- Fabricated columns and frames: Lifted vertically with controlled hoisting to avoid swing or rotation.
- Large welded assemblies and prefabricated components: Irregular pieces requiring steady and precise handling.
- Irregular and long-span steel structures: Trusses, pipe racks, and custom frames demanding high crane span and positioning accuracy.
Q2: How does steel fabrication workflow affect crane selection?
- Frequent short lifts and constant repositioning change crane requirements.
- Precise positioning near cutting, welding, and assembly areas is critical.
- Risk of load rotation during hoisting and trolley travel.
- Shared crane usage across multiple zones, including cutting, fitting, and welding.
Practical takeaway: Cranes must deliver smooth motion and predictable control, not just lifting power.
Q3: Why are overhead cranes considered core production assets in steel workshops?
- Feeding raw steel into cutting and fabrication zones.
- Turning and aligning assemblies during welding.
- Transferring finished structures to finishing or storage areas.
- Supporting trial assembly before site delivery.
Practical takeaway: Downtime in a crane directly affects output and delivery schedules, making reliability essential.
Q4: What local factors influence crane performance in Qatar's steel workshops?
- High temperatures: Affect motors, brakes, and electrical systems.
- Dust and fine particles: From cutting and grinding operations.
- Coastal humidity: Increases risk of corrosion in Doha and Al Wakrah.
Practical takeaway: Cranes need reinforced protection, proper sealing, and suitable duty classification for local conditions.
Q5: What is the main takeaway for selecting overhead cranes in Qatar steel fabrication?
Steel workshops require cranes that support steady, repeatable lifting with precise control. Capacity alone isn't enough; the crane must fit the workflow to ensure efficiency, safety, and reliability.
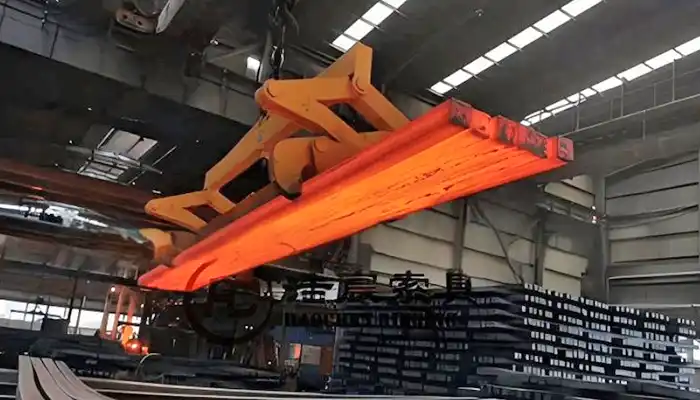 Frequently Asked Questions: Overhead Crane Types in Steel Fabrication
Frequently Asked Questions: Overhead Crane Types in Steel Fabrication
Q1: What are the main overhead crane types used in Qatar's steel fabrication workshops?
Steel workshops typically use different cranes based on load, size, frequency, and indoor/outdoor requirements:
- Double girder overhead cranes: For long beams, heavy assemblies, and frequent lifts.
- Single girder overhead cranes: For lighter loads, smaller workshops, or localized fabrication zones.
- Gantry and semi-gantry cranes: For outdoor yards, pre-assembly areas, or oversized components.
Q2: Why are double girder overhead cranes the most common choice?
- Higher lifting stability for long steel beams and welded frames.
- Better hook approach for lifting near walls and columns.
- Greater lifting height for tall columns or stacked assemblies.
- Strong performance under frequent and medium-to-heavy duty cycles.
Typical applications: Handling 10–50 ton structures, moving long-span beams, and lifting large welded assemblies with minimal swing.
Q3: When are single girder overhead cranes preferred?
- Localized fabrication zones such as cutting or fitting areas.
- Workshops with lower roof heights or smaller lifting requirements.
- Occasional lifting rather than continuous operations.
Key characteristics: Lower cost, reduced structural load, limited hook approach and lifting height. Typically suitable for 5–20 ton loads and smaller steel parts.
Q4: How are gantry and semi-gantry cranes used in steel fabrication?
- Steel yards and outdoor storage areas.
- Pre-assembly of large frames or trusses.
- Handling steel before or after indoor fabrication stages.
Advantages: Semi gantry cranes No need for full overhead runway, flexible coverage, easier expansion, and practical for outdoor conditions with weather protection and corrosion resistance.
Q5: What is the practical takeaway for selecting crane types in Qatar steel workshops?
Double girder cranes handle core production lifting, single girder cranes support lighter zones, and gantry/semi-gantry cranes manage outdoor and yard operations. The right mix balances cost, productivity, and long-term usability.
Frequently Asked Questions: Defining Workshop & Production Requirements
Q1: How does workshop width affect crane selection?
The physical width of your workshop determines the crane span. Proper span ensures safe load distribution, cost efficiency, and operational coverage.
- Measure clear distance between runway beams
- Account for usable width after columns, cable trays, and services
- Decide if full-span coverage is necessary or partial bay coverage is sufficient
Practical tip: Too wide increases cost; too narrow limits workflow.
Q2: What is the correct way to determine required hook lift height?
Lift height is the usable vertical distance from the floor to the hook at its highest safe position.
- Height of stacked steel or jigs
- Size of welded assemblies during trial fit
- Clearance needed above loads for safe travel
Note: Underestimating lift height can prevent lifting your actual production pieces after installation.
Q3: How do maximum and average steel weights influence crane choice?
Both peak and typical loads must be considered:
- Identify the heaviest single piece handled
- Understand average daily lifting weight
- Include the weight of lifting accessories such as clamps or C-hooks
Practical tip: Designing only for peak weight can result in over-capacity cranes that are inefficient and costly to run.
Q4: Why is lifting frequency and shift operation important?
Hoist selection, motor sizing, and duty classification depend on how often lifting occurs:
- Number of lifts per hour
- Single-shift or multi-shift operation
- Continuous vs. intermittent lifting
Practical tip: High-frequency operations require cranes designed for repeated starts and stops to prevent excessive wear.
Q5: How does single-piece vs bundled steel lifting affect crane selection?
- Determine if beams are lifted individually or in bundles
- Calculate maximum bundle weight including rigging
- Assess load stability during travel
Practical tip: Bundled lifting increases capacity demand and affects hook design and hoist speed.
Q6: Why should workshops plan for future expansion?
- Leave space for future crane bays
- Design runway beams for higher capacity upgrades
- Ensure power supply margin for additional cranes
Practical tip: Planning ahead avoids costly modifications and supports long-term production growth.
Q7: What are the common problems if production requirements are not defined?
Without proper assessment, buyers risk:
- Cranes too heavy for routine lifting
- Insufficient lifting height for finished assemblies
- Limited coverage disrupting workflow
Key takeaway: A crane should support productivity, not become a workflow constraint.
Frequently Asked Questions: Technical Specification Checklist for Buyers
Q1: How should I determine the crane's rated capacity?
The crane should exceed your maximum load to account for rigging and uneven steel shapes.
- Maximum single-piece or bundled steel weight
- Weight of rigging, clamps, magnets, or C-hooks
- Include a safety margin above the working load (typically 10–20%)
Example: Lifting a 16-ton beam may require an 18–20 ton crane.
Q2: Why is crane span and runway spacing important?
Span defines coverage across the workshop and affects wheel load and rail wear.
- Distance between runway centerlines
- Column placement and obstructions
- Allowance for future crane upgrades
Tip: Incorrect spacing reduces travel efficiency and increases long-term maintenance.
Q3: How do lift height and hook approach affect operations?
- Net lifting height from floor to hook
- Clearance for tall columns or frames
- Hook approach near walls and ends
Practical insight: Limited hook approach can leave unused workspace and reduce flexibility.
Q4: What is hoist duty classification and why is it critical?
Duty class indicates how hard the crane can work over its lifespan. Selecting the right class avoids premature wear.
- Number of lifts per shift
- Average vs. maximum load
- Length of daily operation
Tip: Light-duty hoists may lift loads but fail under repetitive fabrication cycles.
Q5: How should I evaluate crane travel and hoist speed?
Speed must balance productivity with precise control for assembly work.
- Smooth load handling during welding and assembly
- Trolley and bridge travel speed for material transfer
- Hoist speed suitable for precise positioning
Insight: Steady movement often saves more time than maximum speed.
Q6: What power supply considerations are important for Qatar?
- Voltage and frequency compatibility with local standards
- Control panel and motor protection class
- Cable routing and power feed arrangement
Tip: Electrical mismatches after delivery can delay commissioning and increase costs.
Q7: Why is a complete specification checklist necessary?
Missing specifications often cause inefficiency or unexpected costs:
- Over-designed cranes with unnecessary expense
- Under-performing cranes that limit lifting height or coverage
- Premature wear due to wrong duty class
Takeaway: A full checklist ensures the overhead crane works reliably from day one and supports production long-term.
Frequently Asked Questions: Crane Features for Efficient Steel Fabrication
Q1: How do Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) improve lifting control?
VFDs manage motor acceleration and deceleration, ensuring smooth hoist and trolley motion.
- Smooth start and stop without sudden jerks
- Reduced load swing when handling long beams
- Less stress on gearboxes, ropes, and crane structure
Tip: VFDs extend component life and improve handling precision during repeated lifts.
Q2: What are the benefits of anti-sway and precision positioning systems?
These systems control long steel members during travel, reducing manual intervention and improving efficiency.
- Better control of long beams and frames
- Faster positioning near welding or assembly stations
- Reduced need for ground workers to guide loads
Insight: Anti-sway technology minimizes setup time and improves safety around partially finished structures.
Q3: Why is dual-speed hoisting important for assembly work?
Dual-speed hoists allow both fast transfers and precise placement.
- Faster lifting for material transfers
- Slow, controlled movement for fitting and alignment
- Easier positioning before welding or trial assembly
Practical tip: Choose dual-speed hoists for workshops with frequent trial assembly or heavy frame alignment tasks.
Q4: Which lifting attachments are essential for steel fabrication?
Proper attachments improve safety, reduce rigging time, and ensure balanced lifting.
- Steel clamps for beams and plates
- Electromagnetic lifters for flat steel or stacked sections
- C-hooks for long beams and profiles
Tip: Select the attachment based on steel shape and bundle size for optimal workflow.
Q5: How do control options affect operator performance?
Crane controls impact visibility, safety, and precision in handling.
- Pendant control for fixed workstations
- Wireless remote control for improved visibility and operator mobility
Insight: Wireless control is ideal when operators need to walk with the load or work around large assemblies.
Q6: Why are these features critical for daily fabrication operations?
Modern crane features reduce time, effort, and risk in daily steel handling.
- Minimize rework due to misalignment
- Reduce manual guiding of loads
- Protect welded assemblies from damage
Takeaway: Cranes equipped with these features align with production needs and improve overall fabrication efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions: Environmental & Regulatory Factors for Steel Fabrication Cranes in Qatar
Q1: How should cranes be protected against coastal humidity in Doha and Al Wakrah?
Coastal humidity and salt-laden air accelerate corrosion, even indoors.
- Use anti-corrosion paint systems suitable for industrial environments
- Ensure proper surface preparation before painting
- Protect bolts, wheels, and exposed steel parts
Tip: Proper protection prevents seized components, reduces wear, and lowers maintenance costs.
Q2: Why are dust-protected electrical enclosures necessary?
Steel cutting, grinding, and welding generate fine dust that can damage electrical systems.
- Use electrical enclosures with suitable ingress protection
- Seal motor housings to prevent dust ingress
- Maintain clean and organized cable routing
Insight: Dust buildup is a common cause of overheating and unexpected crane shutdowns.
Q3: What safety and electrical compliance is required in Qatar?
Cranes must meet local safety and electrical regulations to avoid delays or insurance issues.
- Voltage and frequency matching Qatar standards
- Safety devices like limit switches and overload protection
- Proper grounding and emergency stop systems
Practical tip: Confirm compliance during the design stage to prevent costly post-delivery modifications.
Q4: How do heat-resistant motors and components improve crane reliability?
High ambient temperatures increase stress on motors, brakes, and electrical parts.
- Motors rated for high ambient temperatures
- Adequate ventilation and thermal protection
- Heat-resistant cables and insulation materials
Tip: Especially important for multi-shift operations or enclosed workshops to prevent overheating and downtime.
Q5: Why is local adaptation critical for industrial cranes in Qatar?
Cranes not adapted to local conditions often fail prematurely.
- Electrical faults from heat and dust
- Faster corrosion of exposed parts
- Increased downtime and maintenance interventions
Takeaway: Properly adapted cranes provide stable performance, protect investment, and reduce long-term operational risks.
Frequently Asked Questions: Choosing an Overhead Crane Supplier for Steel Fabrication in Qatar
Q1: Why is supplier experience in steel structure crane projects important?
Handling long beams, welded frames, and uneven loads in steel workshops requires specialized knowledge.
- Previous crane projects in steel structure fabrication
- Experience with long-span and heavy-duty workshop cranes
- Understanding repetitive lifting and fabrication workflows
Tip: Suppliers familiar with steel workshops provide practical solutions, not just standard configurations.
Q2: How do CE, ISO, and third-party inspections impact crane quality?
Certification ensures safety, regulatory acceptance, and long-term reliability.
- CE compliance for crane structure and electrical systems
- ISO-certified manufacturing and quality control
- Third-party inspection before shipment
Insight: Inspection reports reduce disputes during installation and commissioning.
Q3: Why is engineering support for custom spans and layouts critical?
Steel workshops rarely follow standard layouts, and columns, bays, or future expansion affect crane design.
- Layout drawings based on actual workshop dimensions
- Load calculations for specific steel components
- Advice on runway beam design and future upgrades
Tip: Strong engineering input reduces costly site modifications later.
Q4: What support should suppliers provide during installation and commissioning?
Even a well-built crane can underperform if installed incorrectly.
- Clear installation instructions and drawings
- Guidance on rail alignment and tolerances
- Support during load testing and commissioning
Tip: Suppliers involved throughout installation ensure the crane performs as designed.
Q5: Why are spare parts availability and technical documentation important?
Cranes operate for years; delayed parts or missing documentation can disrupt production.
- Local or regional availability of critical spare parts
- Clear manuals for operation and maintenance
- Electrical drawings and troubleshooting guides
Tip: Good documentation and parts access enable faster repairs and safer daily operation.
Frequently Asked Questions: Installation, Commissioning & Operator Readiness for Steel Fabrication Cranes in Qatar
Q1: Why is correct runway beam and rail alignment critical?
The runway carries the crane for its entire service life. Even minor alignment errors create mechanical stress and uneven wear.
- Rail straightness and level within tolerance
- Correct spacing between runway beams
- Secure fixation of rails and end stops
Tip: Misaligned rails cause uneven wheel wear, unstable travel, and higher motor loads.
Q2: What should proper load testing and commissioning include?
Before production, cranes must be tested under controlled conditions to verify safety and performance.
- No-load functional testing
- Static and dynamic load testing at rated capacity
- Verification of limit switches and safety devices
- Formal commissioning and load test reports
Insight: Records are essential for safety approval, acceptance, and future audits.
Q3: Why is operator and maintenance team training necessary?
Even a well-installed crane can be unsafe if operators and maintenance staff are unfamiliar with its operation.
- Daily operation and control response
- Load handling practices for beams and assemblies
- Emergency procedures and safety checks
- Routine inspection points for maintenance staff
Tip: Short, focused training prevents misuse, reduces damage, and enhances safety.
Q4: How should maintenance schedules and responsibilities be defined?
Steel fabrication cranes operate under constant load cycles. Proactive maintenance is essential.
- Lubrication schedule for moving parts
- Inspection intervals for ropes, brakes, and wheels
- Clear assignment of responsibilities between operators and maintenance staff
Insight: Documented routines reduce downtime and extend crane life.
Q5: What are the consequences of poor installation?
Even high-quality cranes fail if installed incorrectly.
- Repeated electrical faults
- Premature wear of mechanical components
- Reduced lifting accuracy and higher safety risks
Tip: Proper installation, commissioning, and operator readiness ensure reliable daily performance from day one.
Frequently Asked Questions: Cost, ROI & Long-Term Ownership of Steel Fabrication Cranes in Qatar
Q1: Why is energy efficiency important in daily crane operations?
Steel fabrication cranes perform frequent starts, stops, and short travels. Energy use adds up quickly and affects operating costs.
- Motor efficiency ratings
- Use of VFDs to reduce power spikes
- Smooth acceleration to avoid wasted energy
Insight: Energy-efficient cranes reduce monthly costs while maintaining output.
Q2: How does maintenance frequency affect cost and uptime?
Maintenance cost is linked to design quality and duty classification.
- Correct hoist duty class for repetitive lifting
- High-quality bearings, brakes, and gearboxes
- Accessibility for inspection and servicing
Tip: Poorly designed cranes or wrong duty class increase labor costs and disrupt production schedules.
Q3: What downtime risks should buyers consider?
Crane downtime impacts multiple workstations in steel fabrication.
- Reliability of key electrical components
- Availability of spare parts and service support
- Ease of troubleshooting and repair
Insight: Even short downtime delays welding, assembly, and dispatch, reducing overall productivity.
Q4: How can cranes be prepared for future production changes?
Workshops often evolve with heavier components, longer spans, or higher output. Planning for adaptability protects the investment.
- Capacity or hoist upgrades without full replacement
- Integration of additional control features
- Compatibility with expanded runway systems
Tip: Future-ready cranes avoid premature replacement and maintain productivity as the workshop grows.
Q5: What is the true measure of crane value?
The real cost is the cost per lift over the crane's lifetime, not the initial purchase price.
- Lower energy consumption per operation
- Fewer breakdowns and service interventions
- Stable performance under real workshop conditions
Insight: Properly specified cranes deliver lower total cost of ownership and higher ROI for steel fabrication workshops.
Buyer FAQs: Selecting Overhead Cranes for Steel Fabrication in Qatar
Q1: What type of overhead crane is best for steel structure fabrication in Qatar?
Workshops handle beams, columns, and trusses of varying lengths and weights. The choice depends on layout and lifting needs:
- Single girder cranes – suitable for lighter loads and smaller workshops
- Double girder cranes – recommended for heavy, long, or frequent lifts due to better stability and higher lifting height
Q2: How do workshops in Doha, Al Wakrah, and Al Daayen choose crane capacity correctly?
Capacity selection should be based on actual work, not just theoretical weight:
- Determine maximum single-piece or bundled steel weight
- Include lifting accessories like clamps or C-hooks
- Apply a 20–30% safety margin to prevent overloading
Accurate calculations prevent over-specification, reducing unnecessary cost while ensuring safety.
Q3: What crane specifications directly affect handling of beams, columns, and trusses?
- Span and runway length – must match workshop dimensions
- Lifting height – adequate clearance for stacked or long steel sections
- Trolley speed and travel range – impacts efficiency in material movement
- Hoist type – wire rope hoists for heavy loads, chain hoists for lighter items
Q4: How do environmental factors (heat, dust, corrosion) influence crane design?
Qatar's climate requires cranes adapted for harsh conditions:
- Special anti-corrosion coatings for steel structures
- Dust-resistant motors and electrical enclosures
- Heat-tolerant components to handle high ambient temperatures
Local adaptation ensures reliable operation and reduces maintenance issues.
Q5: What should buyers check before approving an overhead crane supplier?
- CE, ISO, or other internationally recognized certifications
- Proven experience with steel fabrication projects
- After-sales support, spare parts availability, and maintenance services
- Customization options for local environmental conditions
Q6: How can steel fabricators avoid overspending while future-proofing crane systems?
- Match capacity to actual lifting needs with a modest safety margin
- Choose modular crane designs to allow easy upgrades
- Consider energy-efficient motors and automation-ready features
- Verify runway and crane layout can accommodate future expansion without costly rework
Conclusion: Making the Right Overhead Crane Investment
For steel structure fabrication workshops in Al Daayen, Al Wakrah, and Doha, purchasing an overhead crane is more than buying a piece of equipment—it’s a long-term production decision. The crane you choose directly affects workflow efficiency, safety, and overall project timelines.
The right crane achieves several practical goals:
- Matches real lifting workflows – It handles your beams, frames, and welded assemblies as they are actually moved in the workshop.
- Fits current and future workshop layouts – Adequate span, hook height, and runway design accommodate both today’s work and planned expansion.
- Performs reliably in Qatar’s environment – Corrosion protection, dust-proofing, and heat-resistant components keep operations stable.
- Minimizes lifecycle cost and operational risk – Proper duty classification, energy efficiency, and maintenance planning reduce downtime and overall expenses.
In short, buyers who focus on application-driven specifications—rather than simply looking at crane tonnage—end up with safer operations, smoother workflow, and better returns over the crane’s lifetime. A well-chosen crane is not just equipment; it is an investment in consistent, high-quality steel fabrication.