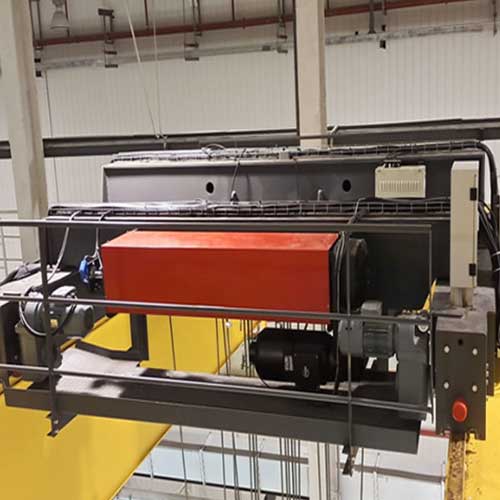
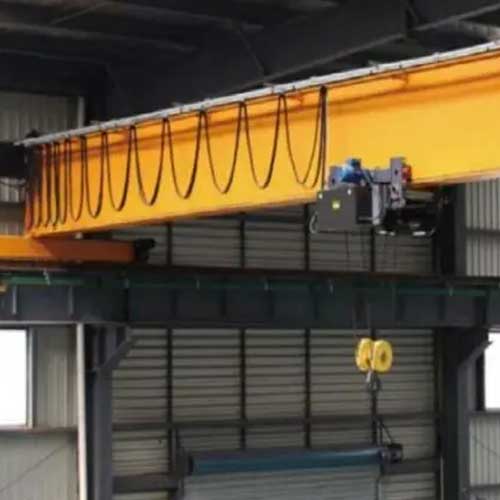
Electric Hoist Auxiliary Hoist, Overhead Crane with Auxiliary Hoist
An auxiliary hoist is a secondary lifting mechanism in cranes, boosting lifting capabilities and versatility for efficient industrial operations.
Category: Overhead Hoist
Your Trusted Overhead Hoist Manufacturer & Supplier
Electric Hoist Auxiliary Hoist, Overhead Crane with Auxiliary Hoist
An auxiliary hoist is a secondary lifting mechanism in cranes, boosting lifting capabilities and versatility for efficient industrial operations.
An auxiliary hoist is a lifting device commonly used in various industrial applications to enhance the lifting capabilities of cranes or hoisting systems. It serves as an additional lifting mechanism alongside the main hoist and is designed to handle specific tasks or loads that may require different lifting capacities or precision.
An auxiliary hoist is a supplementary lifting mechanism integrated with cranes or hoisting systems, working in tandem with the main hoist to provide enhanced lifting capabilities and versatility in industrial applications. It allows for dual lifting operations, increased adaptability, and improved efficiency, making it a crucial component in optimizing various lifting tasks across different industries.
Key features of an auxiliary hoist include:
- Dual Lifting Capability: An auxiliary hoist works in conjunction with the main hoist, providing dual lifting capabilities. This enables the crane or hoisting system to handle multiple loads simultaneously or perform complex lifting operations.
- Enhanced Versatility: Auxiliary hoists add versatility to lifting operations by allowing for different lifting speeds, capacities, and functionalities. This adaptability makes them suitable for a wide range of industrial tasks.
- Customization Options: Depending on the design and type, auxiliary hoists often offer customization options. Users can tailor the auxiliary hoist system to meet specific lifting requirements, such as adjusting lifting speeds or choosing specific features.
- Application in Various Industries: Auxiliary hoists find applications in diverse industries, including manufacturing, construction, warehousing, and logistics. They play a crucial role in optimizing lifting operations and improving overall efficiency in industrial settings.
- Integration with Hoisting Systems: Typically, auxiliary hoists are integrated into cranes or hoisting systems, either as part of an overhead crane or an open winch system. This integration allows for seamless coordination between the main and auxiliary hoists during lifting operations.
- Safety Features: Modern auxiliary hoists are equipped with advanced safety features to ensure secure and reliable lifting. These may include emergency stop systems, load-limiting devices, and collision avoidance systems.
In summary, an auxiliary hoist is a valuable component in lifting technology, providing additional lifting capabilities and enhancing the versatility of hoisting systems in various industrial applications. Its integration with main hoists contributes to efficient and precise lifting operations, making it an essential tool in modern industrial settings.
Essentials of Auxiliary Hoists: Understanding the Core Functionality and Significance
At its core, an Auxiliary Hoist is a sophisticated lifting mechanism designed to amplify the lifting capabilities of cranes. It's the silent force behind the scenes, working tirelessly to hoist and maneuver heavy loads with precision and efficiency. The cable systems, drums, and motors intricately choreograph a dance of strength, enabling the hoist to undertake tasks that would otherwise be daunting.
But it's not just about the raw power; it's about control. The precision with which an Auxiliary Hoist operates is what sets it apart. From delicate material handling in manufacturing to the robust demands of construction projects, this lifting marvel adapts to diverse scenarios with finesse.
The Power Within: How Auxiliary Hoists Enhance Lifting Capabilities
Imagine the lifting capacity of your existing crane multiplied, effortlessly handling heavier loads and streamlining your operations. That's the power within an Auxiliary Hoist. By complementing the main hoist, it transforms your lifting experience, making it not just efficient but also remarkably versatile.
As we delve deeper into the types of Auxiliary Hoists, the spotlight will shift to the marvels of modularity and the brilliance of builtup structures, each catering to specific needs and applications.
Types of Auxiliary Hoists
Auxiliary Hoists aren't a one-size-fits-all solution. They come in various types, each crafted to address specific challenges and excel in distinct applications. Let's explore the two prominent categories: Modular Marvels and Builtup Brilliance.
Modular Marvels: Exploring the Benefits and Customization Features of Modular Auxiliary Hoists
Picture a lifting system that adapts to your needs, evolves with your operations, and delivers efficiency in a modular package. That's the essence of Modular Auxiliary Hoists. These marvels of engineering bring customization to the forefront, offering a scalable solution that grows with your demands.
Benefits:
Scalability: Easily adjust the lifting capacity by adding or removing modules.
Ease of Maintenance: Replace or upgrade components without significant disruption.
Customization Features:
Tailored Configurations: Customize the hoist based on spatial constraints.
Application-specific Features: Equip with specialized features for diverse industrial tasks.
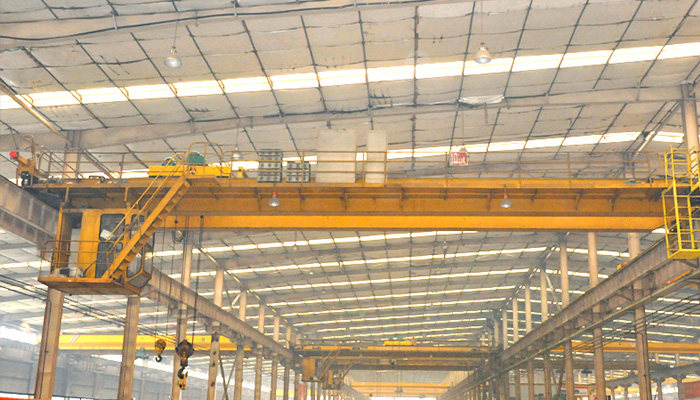

CD/MD Main and Auxiliary Hoist Crane:
Design Features:
CD (Single Speed) or MD (Dual Speed) Hoists:
CD hoists operate at a single fixed speed, suitable for routine lifting tasks.
MD hoists offer dual-speed options, providing precision in delicate operations and efficiency in heavier lifts.
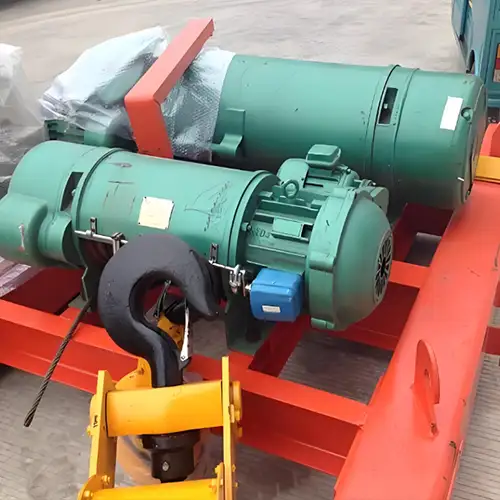
Auxiliary Hoist for Additional Lifting:
Integration of an auxiliary hoist alongside the main hoist system.
Enables additional lifting tasks, contributing to the crane's versatility.
Typical Applications:
Commonly Used in General Industrial Settings:
Well-suited for a wide range of industrial applications due to its versatility.
Finds applications in manufacturing, warehousing, and other general industrial settings.
Tasks Requiring Both Main and Auxiliary Lifting:
Ideal for operations where both main and auxiliary lifting capabilities are necessary.
Offers flexibility in handling various loads and tasks within an industrial environment.
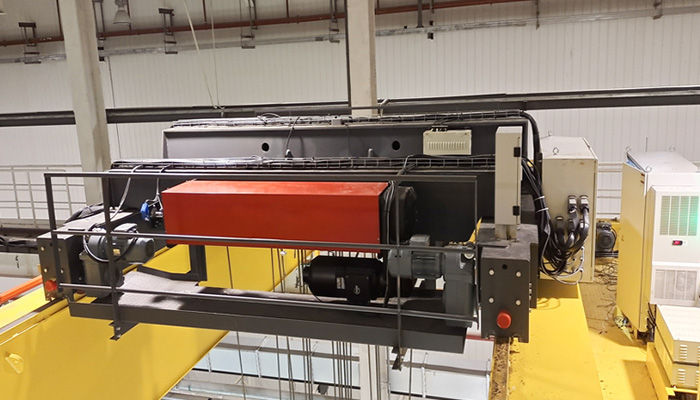

Low Headroom Main and Auxiliary Hoist Crane:
Design Features:
Specifically Designed for Limited Headroom:
Tailored design to accommodate applications with limited vertical space.
Ensures efficient use of available headroom within the facility.
Compact Design with Reduced Distance:
Features a compact overall design.
Reduces the distance between the beam and the hook, optimizing space utilization.
Utilizes Low Headroom Trolleys:
Incorporates low headroom trolleys for efficient load movement in constrained spaces.
Enables the crane to operate effectively within limited vertical clearances.
Typical Applications:
Ideal for Facilities with Limited Space:
Suited for environments where space is limited or ceiling clearance is a constraint.
Provides an effective lifting solution without compromising on efficiency in confined spaces.
Commonly Used in Workshops, Warehouses, and Manufacturing Plants:
Finds applications in workshops, warehouses, and manufacturing plants.
Particularly beneficial in settings where maximizing vertical space is crucial for workflow optimization.
CD/MD Main and Auxiliary Hoist Cranes and Low Headroom Main and Auxiliary Hoist Cranes cater to specific operational needs, offering tailored solutions for different industrial scenarios. Whether it's the versatility of CD/MD cranes in general settings or the space optimization of low headroom cranes in confined spaces, both types contribute to efficient and precise lifting operations.
Let's compare CD/MD Modular Auxiliary Hoists with Low Headroom Modular Auxiliary Hoists based on key factors:
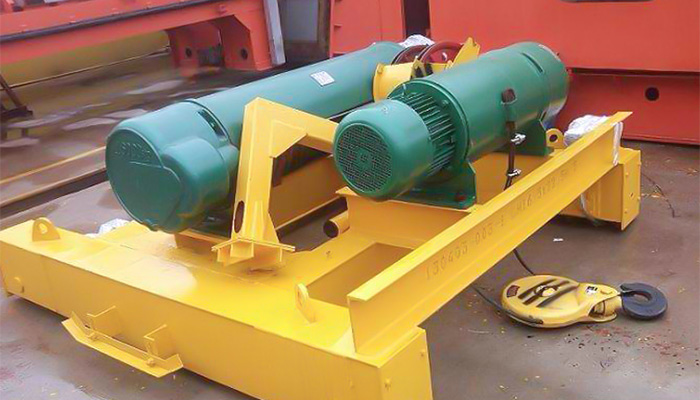

CD/MD Modular Auxiliary Hoists:
Design and Speed Options:
CD (Single Speed) Hoists:
Operate at a single fixed speed.
Suitable for routine lifting tasks in various industrial applications.
MD (Dual Speed) Hoists:
Offer dual-speed options for precision and efficiency.
Ideal for delicate operations and heavier lifts.
Auxiliary Lifting:
Equipped with an auxiliary hoist for additional lifting tasks.
Provides versatility in handling various loads within an industrial setting.
Typical Applications:
Commonly used in general industrial settings.
Suitable for tasks requiring both main and auxiliary lifting operations.
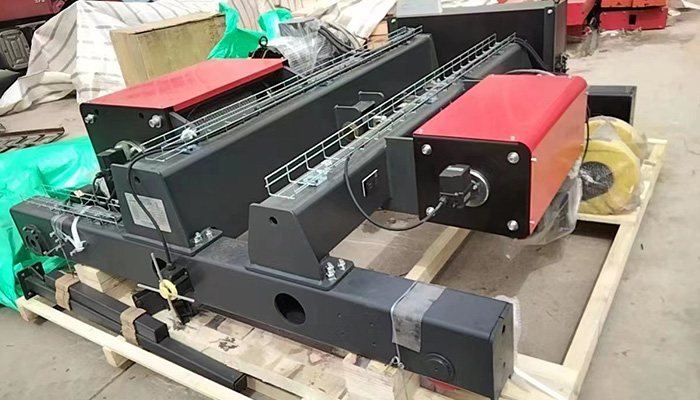
Low Headroom Modular Auxiliary Hoists:
Design and Space Optimization:
Specifically designed for applications with limited headroom.
Compact design with a reduced distance between the beam and the hook.
Low Headroom Trolleys:
Utilizes low headroom trolleys for efficient use of vertical space.
Enables the crane to operate effectively in environments with constrained vertical clearances.
Typical Applications:
Ideal for facilities with limited space or low ceiling clearance.
Commonly used in workshops, warehouses, and manufacturing plants where maximizing vertical space is crucial.
Comparison:
Versatility:
CD/MD Modular Auxiliary Hoists:
Versatile in handling a broad range of industrial tasks.
Offers flexibility with both single-speed and dual-speed options.
Low Headroom Modular Auxiliary Hoists:
Tailored for specific applications with limited headroom.
Ideal for environments where space optimization is a critical factor.
Space Optimization:
CD/MD Modular Auxiliary Hoists:
Suited for various industrial settings.
Offers versatility without specific emphasis on low headroom constraints.
Low Headroom Modular Auxiliary Hoists:
Specifically designed to optimize space in environments with limited headroom.
Efficient in confined spaces where maximizing vertical clearance is essential.
Typical Applications:
CD/MD Modular Auxiliary Hoists:
Commonly used in general industrial settings requiring a combination of main and auxiliary lifting capabilities.
Low Headroom Modular Auxiliary Hoists:
Ideal for specific applications where low headroom is a constraint.
Commonly found in workshops, warehouses, and manufacturing plants with limited vertical clearance.
In summary, CD/MD Modular Auxiliary Hoists offer versatility in various industrial settings, while Low Headroom Modular Auxiliary Hoists are specifically designed for optimizing space in environments with limited headroom. The choice between the two depends on the specific requirements and constraints of the application.
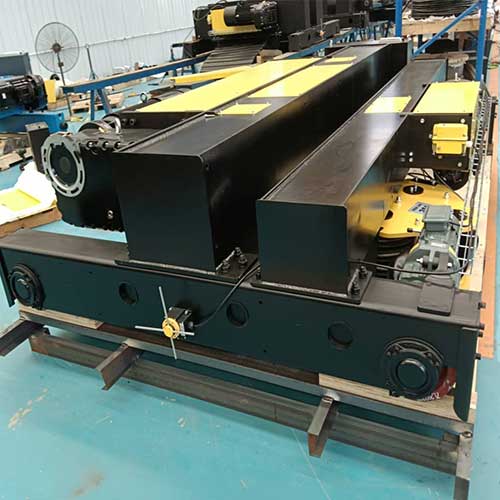
Builtup Auxiliary Hoists
Builtup Auxiliary Hoists embrace a different approach, with an integrated and robust structure. These hoists excel in stability and durability, making them the preferred choice for heavy-duty lifting in various settings.
Structural Characteristics:
Rigidity and Stability: Enhanced stability for precise lifting operations.
Robust Construction: Suited for demanding environments like construction sites.
Versatile Applications:
Heavy-duty Applications: Ideal for lifting large and unwieldy loads.
Fixed Installations: Well-suited for consistent lifting requirements over time.
As we navigate through the intricacies of each type, the focus will shift to their unique features, benefits, and applications, providing you with the insights needed to make informed decisions for your lifting needs. Stay tuned for the next installment, where we unravel the tailored excellence of these extraordinary lifting solutions.
Traditional built up auxiliary hoists for open winch crane vs. European style auxiliary hoist for open winch crane
Let's compare Traditional Built-Up Auxiliary Hoists for Open Winch Cranes with European Style Auxiliary Hoists for Open Winch Cranes based on key factors:

Traditional Built-Up Auxiliary Hoists:
Design and Construction:
Built-Up Design:
Utilizes a traditional built-up design for the auxiliary hoist system.
Typically characterized by robust and sturdy construction to handle heavy-duty lifting tasks.
Load Capacity:
Heavy-Duty Lifting:
Well-suited for heavy-duty lifting operations.
Designed to handle substantial loads in industrial settings such as manufacturing and construction.
Customization:
Limited Customization:
May have limited customization options compared to European style hoists.
Generally designed with a focus on strength and durability.
Common Applications:
Industrial Settings:
Commonly found in traditional industrial settings with a demand for heavy-duty lifting.

European Style Auxiliary Hoists:
Design and Construction:
Compact and Lightweight Design:
Features a compact and lightweight design, emphasizing efficiency and adaptability.
Utilizes modern engineering for optimized performance.
Load Capacity:
Variable Load Handling:
Suited for variable load handling, including both light and heavy loads.
Offers flexibility to adapt to different lifting requirements.
Customization:
High Customization Options:
Typically offers higher customization options to meet specific user requirements.
Allows for tailoring the hoist system based on the application's unique needs.
Common Applications:
Diverse Industrial Applications:
Commonly found in a wide range of industrial applications due to its adaptability.
Suitable for various industries, including manufacturing, logistics, and more.
Comparison:
Strength and Load Handling:
Traditional Built-Up Auxiliary Hoists:
Known for strength and suitability for heavy-duty lifting tasks.
Designed for applications where handling substantial loads is a primary requirement.
European Style Auxiliary Hoists:
Balances strength with adaptability, catering to a broader range of load handling needs.
Offers versatility for both light and heavy load applications.
Design Philosophy:
Traditional Built-Up Auxiliary Hoists:
Emphasizes traditional and robust construction for durability.
May be preferred in settings with consistent heavy load requirements.
European Style Auxiliary Hoists:
Focuses on a modern, compact design to optimize performance.
Suited for environments where adaptability and efficiency are crucial.
Application Flexibility:
Traditional Built-Up Auxiliary Hoists:
Well-suited for specific heavy-duty applications.
May have limited adaptability compared to European style hoists.
European Style Auxiliary Hoists:
Adaptable to a wide range of applications, offering flexibility in load handling.
Suitable for diverse industries with varying lifting needs.
The choice between Traditional Built-Up Auxiliary Hoists and European Style Auxiliary Hoists depends on the specific requirements of the application, including load handling, customization needs, and the desired balance between strength and adaptability.
Features, Benefits, and Applications
Tailored Excellence for Every Task
Auxiliary Hoists, with their tailored design, bring a level of excellence that aligns perfectly with diverse industrial needs. In this section, we dissect the features, benefits, and applications of both Modular Marvels and Builtup Brilliance.
Modular Marvels Unveiled:
a. Customization Capabilities: Tailoring the Hoist to Your Specific Needs
Modular Auxiliary Hoists redefine adaptability with their customizable nature. The ability to tailor the hoist to your specific needs ensures that you're not investing in excess capacity or compromising on lifting capabilities.
Benefits:
Cost-Effective Scaling: Add or remove modules based on fluctuating demands, optimizing costs.
Efficiency Boost: Adapt the hoist to handle diverse loads, promoting operational efficiency.
b. Versatility in Action: Showcasing the Varied Applications, from Manufacturing to Construction
The versatility of Modular Auxiliary Hoists comes to life in their diverse applications. From the precision demands of manufacturing processes to the robust lifting requirements of construction, these marvels showcase their prowess in various industrial settings.
Applications:
Manufacturing Precision: Handle delicate materials with finesse, ensuring precision in manufacturing.
Construction Efficiency: Adapt to fluctuating load demands in construction projects, enhancing efficiency.
Builtup Brilliance at Work:
a. Structural Stability: Ensuring Stability in Challenging Environments
Builtup Auxiliary Hoists boast structural stability that stands resilient even in challenging environments. The robust construction ensures that stability is not compromised, making them ideal for heavy-duty lifting in demanding scenarios.
Benefits:
Reliability in Rigorous Environments: Maintain stability and reliability in outdoor or harsh conditions.
Consistent Performance: Excel in heavy-duty applications where stability is paramount.
b. Applications Unleashed: Highlighting Outdoor Applications and Adaptability
Builtup Auxiliary Hoists unleash their potential in various applications, particularly excelling in outdoor settings. The adaptability of these hoists makes them indispensable for lifting in outdoor environments where conditions can be unpredictable.
Applications:
Outdoor Construction: Lift and maneuver heavy materials in construction projects conducted in open spaces.
Yard Operations: Adapt to diverse lifting requirements in outdoor storage yards, providing flexibility.
As we delve into the tailored excellence of Modular Marvels and Builtup Brilliance, it becomes evident that the design intricacies are not just features; they are solutions tailored to meet the specific demands of each industrial task. The journey continues as we explore the typical industrial applications of these exceptional lifting solutions. Stay tuned to witness how Auxiliary Hoists power industrial progress across various sectors.
Modular auxiliary hoist VS Built up auxiliary hoist
Let's compare Modular Auxiliary Hoists with Built-Up Auxiliary Hoists based on key factors:

Modular Auxiliary Hoist:
Design and Construction:
Modular Design:
Utilizes a modular design approach, where components are designed to be easily assembled and disassembled.
Typically characterized by interchangeable parts and flexibility in configuration.
Customization:
High Customization Options:
Offers high customization options to tailor the hoist system based on specific user requirements.
Users can choose and assemble components to meet their unique lifting needs.
Installation and Maintenance:
Ease of Installation:
Generally easier to install due to the modular nature of components.
Offers simplicity in maintenance as individual modules can be replaced or upgraded.
Adaptability:
Versatility and Adaptability:
Suited for diverse applications, providing versatility and adaptability to different lifting scenarios.
Ideal for users with changing or evolving lifting requirements.
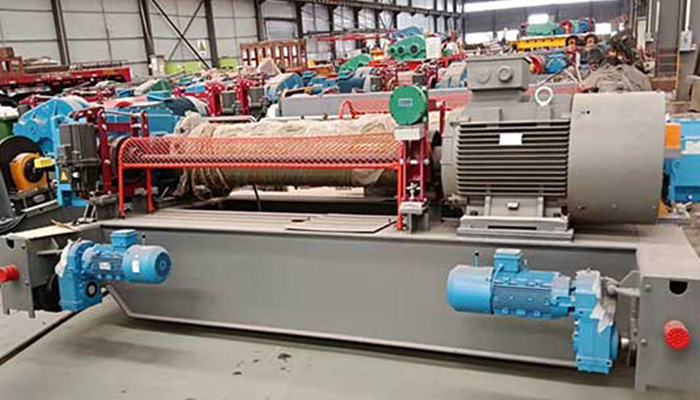

Built-Up Auxiliary Hoist:
Design and Construction:
Integrated Built-Up Design:
Features an integrated built-up design where components are assembled as a single unit.
Characterized by robust construction, often designed for heavy-duty lifting tasks.
Customization:
Limited Customization:
May have limited customization options compared to modular hoists.
Customization is often constrained by the integrated design.
Installation and Maintenance:
Complex Installation:
Installation may be more complex compared to modular hoists due to the integrated nature of components.
Maintenance may involve addressing the entire integrated system.
Adaptability:
Specific Application Focus:
Typically designed for specific applications or industries with consistent lifting requirements.
May be less adaptable to changes in lifting needs compared to modular hoists.
Comparison:
Flexibility and Adaptability:
Modular Auxiliary Hoist:
Offers high flexibility and adaptability to diverse lifting scenarios.
Ideal for users with evolving or changing lifting requirements.
Built-Up Auxiliary Hoist:
More focused on specific applications with less adaptability to changing needs.
Suited for industries with consistent and specific lifting demands.
Customization:
Modular Auxiliary Hoist:
Provides extensive customization options, allowing users to configure the hoist system according to their unique needs.
Built-Up Auxiliary Hoist:
Customization options may be more limited, as the design is often more standardized.
Installation and Maintenance:
Modular Auxiliary Hoist:
Generally easier to install and maintain due to the modular and interchangeable nature of components.
Built-Up Auxiliary Hoist:
Installation and maintenance may be more complex due to the integrated design.
The choice between Modular and Built-Up Auxiliary Hoists depends on factors such as the specific lifting requirements, the need for customization, adaptability to changing scenarios, and the user's preference for installation and maintenance ease.
Typical Industrial Applications
Auxiliary Hoists emerge as the driving force behind industrial progress, revolutionizing the way lifting operations are conducted. Let's delve into two key sectors where the impact of these lifting marvels is most pronounced.
In Construction : How Auxiliary Hoists Streamline Lifting in Construction Projects
Construction projects demand a delicate balance between precision and power. Auxiliary Hoists step into the spotlight in construction scenarios, streamlining lifting operations and contributing to the efficiency of the entire project.
Contributions in Construction:
Heavy Material Maneuvering: Efficiently lift and position heavy materials such as steel beams and construction components.
Spatial Optimization: Overhead and Gantry Cranes with Auxiliary Hoists maximize vertical and horizontal space, crucial in construction sites with limited areas.
Efficiency Unleashed:
Reduced Downtime: Streamlining lifting operations minimizes downtime, contributing to faster construction timelines.
Precision Handling: The synchronized movements of dual hoist systems ensure precise positioning of materials, enhancing overall construction efficiency.
Manufacturing Precision: The Role of Auxiliary Hoists in Optimizing Manufacturing Processes
In the intricate world of manufacturing, precision is paramount. Auxiliary Hoists play a pivotal role in optimizing manufacturing processes, ensuring that lifting operations align seamlessly with the demands of precision manufacturing.
Contributions in Manufacturing:
Delicate Material Handling: Modular Auxiliary Hoists excel in handling delicate materials with finesse, vital in manufacturing intricate components.
Efficient Assembly Line Operations: Builtup Auxiliary Hoists provide the stability needed for lifting heavy components during assembly processes.
Optimization Achieved:
Versatility in Applications: The adaptability of Modular Auxiliary Hoists allows them to cater to a variety of manufacturing tasks, from electronics to automotive.
Enhanced Productivity: Auxiliary Hoists contribute to the overall productivity of manufacturing processes by ensuring smooth and efficient material handling.
As we witness the impactful applications of Auxiliary Hoists in construction and manufacturing, it becomes evident that these lifting solutions are not just tools; they are catalysts for progress. The journey continues as we address the concerns of users and provide tailored solutions in the next segment. Stay tuned to discover how Auxiliary Hoists are designed to address challenges and ensure a seamless lifting experience.
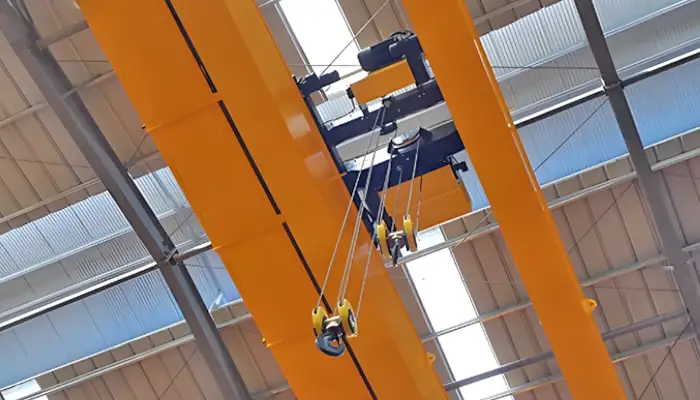

20 Ton/10 Ton Overhead Cranes with Auxiliary Hoist
This is a 20-ton/10-ton, 10-meter Europe-style double girder overhead crane equipped with an auxiliary electric hoist for enhanced material handling in workshops. Key features include:
Main Hoist Capacity: 20 tons for heavy lifting and primary operations.
Auxiliary Hoist Capacity: 10 tons for secondary lifting tasks, providing flexibility and efficiency.
Span: 10 meters, suitable for various workshop dimensions.
Design: Europe-style double girder configuration ensures durability and stability.
Electric Hoist: Facilitates precise and smooth lifting operations.
Quality : Engineered to high standards, combining functionality with a visually appealing design.
Competitive Pricing: Offers exceptional value for top-quality performance.
Ideal for industrial settings, this overhead crane is designed to streamline material handling processes while ensuring safety and reliability.
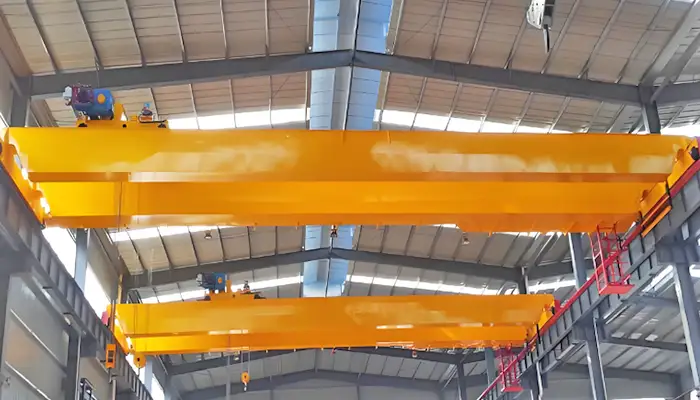

25 Ton /10 Ton Double Girder Overhead Crane with Auxiliary Hook
This overhead crane has a main load capacity of 25 tons and an auxiliary load capacity of 10 tons. Key specifications and features include:
Main Load Capacity: 25 tons, suitable for heavy lifting tasks.
Auxiliary Load Capacity: 10 tons, for additional lifting flexibility.
Span: 19.5 meters, providing a broad coverage area.
Height of Lift (HOL): 9 meters, allowing significant vertical reach.
Design: Europe-style based on FEM standards, ensuring robust construction and safety.
Components:
Crane Trolley (Winch Trolley): Ensures smooth and efficient load handling.
End Truck: Provides stability and support for crane movement.
Bridge Girder: Ensures structural integrity and supports the trolley.
Electrical System: Facilitates precise control and reliable operation.
This crane is engineered for top performance and durability, making it ideal for various industrial applications.
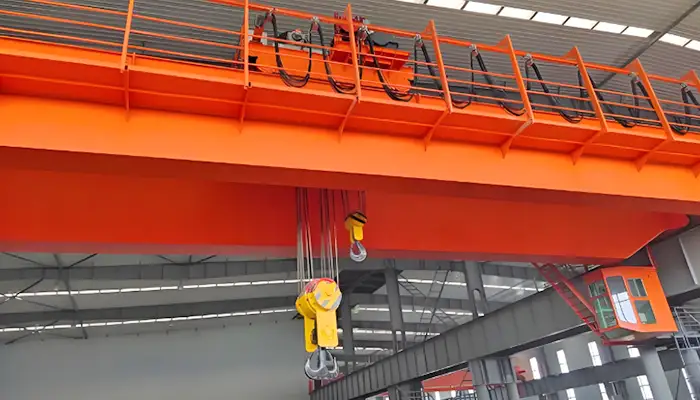

50 Ton /10 Ton Double Girder Overhead Crane with Auxiliary Hook
This overhead crane has a main load capacity of 50 tons and an auxiliary load capacity of 10 tons. Key specifications and features include:
Main Load Capacity: 50 tons for handling heavy-duty lifting tasks.
Auxiliary Load Capacity: 10 tons for additional lifting requirements.
Span: 19.5 meters, offering extensive coverage.
Height of Lift (HOL): 9 meters, providing significant vertical reach.
Design: Europe-style based on FEM standards, ensuring high quality and safety.
Components:
Crane Trolley (Winch Trolley): Ensures efficient and precise load handling.
End Truck: Provides stability and smooth movement along the runway.
Bridge Girder: Ensures robust support for the trolley and load.
Electrical System: Facilitates accurate control and reliable operation.
Control Methods:
Cabin Control: Full field of view, suspended under the main girder, offering comprehensive visibility and control.
Pendant Control: Allows manual operation from the ground.
Remote Control: Provides flexibility and safety by enabling operation from a distance.
This crane is designed for optimal performance and durability, making it ideal for heavy industrial applications.
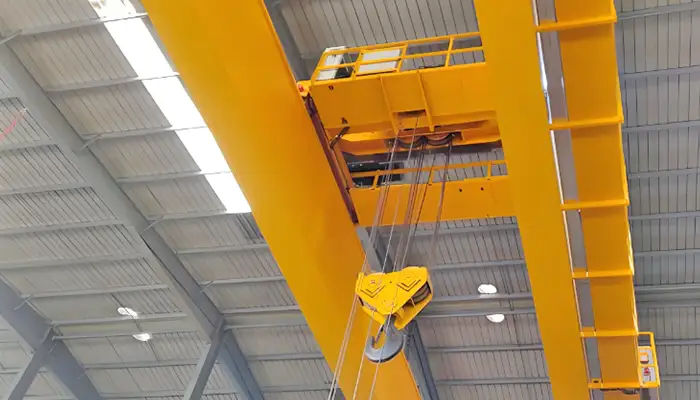

80 Ton /20 Ton Overhead Crane with Auxiliary Hook
This overhead crane has a main load capacity of 80 tons and an auxiliary load capacity of 20 tons. Key specifications and features include:
Main Load Capacity: 80 tons for extremely heavy lifting tasks.
Auxiliary Load Capacity: 20 tons for additional lifting needs.
Span: 20 meters, providing extensive coverage.
Height of Lift (HOL): 10 meters, allowing substantial vertical reach.
Design: Europe-style based on FEM standards, ensuring superior quality and safety.
Components:
Crane Trolley (Winch Trolley): Ensures efficient and precise load handling.
End Truck: Provides stability and smooth movement along the runway.
Bridge Girder: Ensures robust support for the trolley and load.
Electrical System: Facilitates accurate control and reliable operation.
Control Methods:
Cabin Control: Full field of view, suspended under the main girder, offering comprehensive visibility and control.
Pendant Control: Allows manual operation from the ground.
Remote Control: Provides flexibility and safety by enabling operation from a distance.
This crane is engineered for optimal performance and durability, making it ideal for the most demanding industrial applications.
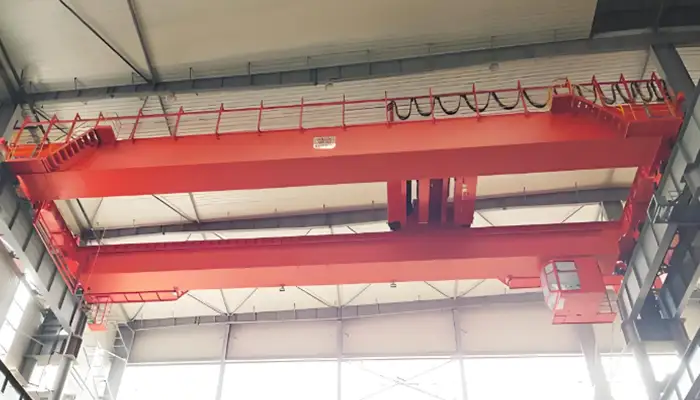

160 Ton/50 Ton Overhead Crane with Auxiliary Hook for Power Plant
This overhead crane has a main load capacity of 160 tons and an auxiliary load capacity of 50 tons. Key specifications and features include:
Main Load Capacity: 160 tons, ideal for handling extremely heavy loads.
Auxiliary Load Capacity: 50 tons, providing additional lifting capacity.
Span: 30 meters, offering extensive coverage.
Height of Lift (HOL): 30 meters, enabling significant vertical reach.
Design: Europe-style, ensuring high quality and safety standards, tailored for electricity plant operations.
Primary Use: Designed primarily for maintaining power transformers in a power plant.
Components:
Crane Trolley (Winch Trolley): Ensures efficient and precise load handling.
End Truck: Provides stability and smooth movement along the runway.
Bridge Girder: Ensures robust support for the trolley and load.
Electrical System: Facilitates accurate control and reliable operation.
This crane is engineered for optimal performance and durability, making it ideal for the demanding maintenance tasks in a power plant.
User Concerns and Solutions
A. Addressing the Top Concerns
Users of Auxiliary Hoists often encounter specific challenges that can impact the efficiency and reliability of lifting operations. Let's explore the top concerns and the innovative solutions embedded in these lifting solutions.
Load Variations Unleashed:
a. Challenge: Handling Fluctuating Loads
One of the primary concerns users face is the unpredictable nature of load variations. Fluctuating loads can pose challenges in maintaining operational efficiency and adapting to changing lifting requirements.
b. Solution: The Adaptability of Modular Auxiliary Hoists
Modular Auxiliary Hoists come to the rescue in scenarios where loads vary. The adaptability of these hoists allows users to scale the lifting capacity effortlessly. Adding or removing modules ensures that the hoist aligns perfectly with the fluctuating demands of the task at hand.
Benefits:
Cost-Effective Adjustments: Scale the hoist capacity based on immediate requirements, optimizing costs.
Operational Efficiency: Adapt to fluctuating loads without compromising on operational efficiency.
Environmental Resilience:
a. Challenge: Coping with Harsh Outdoor Conditions
Outdoor environments can be unforgiving, with harsh weather conditions posing a challenge to the reliability of lifting equipment. Users often face concerns related to the resilience of Auxiliary Hoists in such conditions.
b. Solution: The Robustness of Builtup Auxiliary Hoists and Protective Measures
Builtup Auxiliary Hoists are designed with robust structures that can withstand the rigors of outdoor environments. Their stability and durability make them resilient in the face of challenging conditions. Additionally, protective measures, such as weather-resistant coatings, further enhance the hoist's ability to cope with environmental challenges.
Benefits:
Reliable Outdoor Performance: Builtup Auxiliary Hoists excel in outdoor applications, providing consistent performance.
Extended Equipment Lifespan: Protective measures ensure longevity, reducing the impact of environmental factors on the hoist.
By addressing concerns related to load variations and environmental resilience, Auxiliary Hoists assure users of a reliable and adaptable lifting experience. The journey continues as we dive into the intricacies of user inquiries, exploring common questions and providing insightful answers about these advanced lifting solutions. Stay tuned for an enlightening Q&A session on Auxiliary Hoists.
Questions and Answers on Auxiliary Hoists
Your Curiosities Answered
Curiosity fuels innovation, and when it comes to Auxiliary Hoists, your questions pave the way for a deeper understanding. Let's unravel the mysteries and provide insightful answers to your most pressing inquiries.
How Do Auxiliary Hoists Enhance Lifting Capacity?
Auxiliary Hoists enhance lifting capacity by complementing the main hoist of a crane. They amplify the crane's power, allowing it to effortlessly handle heavier loads. The additional lifting force provided by the Auxiliary Hoist ensures a significant boost in overall lifting capabilities, making it an indispensable tool in various industrial applications.
What Sets Modular Auxiliary Hoists Apart in Customization?
Modular Auxiliary Hoists stand out in customization due to their scalable design. These hoists are built with modular components that can be easily added or removed, tailoring the hoist to specific lifting requirements. The ability to customize the hoist's capacity and features makes it a versatile and cost-effective solution for industries with dynamic lifting needs.
Where Do Builtup Auxiliary Hoists Excel in Terms of Applications?
Builtup Auxiliary Hoists excel in applications that demand structural stability and durability. Their robust construction makes them ideal for heavy-duty lifting in challenging environments. Builtup Auxiliary Hoists are commonly used in outdoor construction projects, where stability and reliability are paramount, ensuring consistent performance in demanding conditions.
How Are Concerns About Load Variations Addressed with Auxiliary Hoists?
Concerns about load variations are effectively addressed with the adaptability of Modular Auxiliary Hoists. These hoists can be easily adjusted to handle fluctuating loads by adding or removing modules. This scalable solution ensures that the hoist aligns precisely with the changing demands of the task at hand, optimizing efficiency and minimizing downtime.
What Safety Measures Are Embedded in Auxiliary Hoists for Industrial Use?
Auxiliary Hoists prioritize safety through various embedded measures, including emergency stop systems and load-limiting devices. Emergency stop systems enable swift responses to unforeseen situations, ensuring the immediate halting of lifting operations. Load-limiting devices prevent overloads, enhancing safety during lifting tasks. Additionally, collision avoidance systems and operator training contribute to the overall safety of Auxiliary Hoists in industrial settings.
As we address your curiosities about Auxiliary Hoists, it's evident that these lifting solutions are not just about power; they are about precision, adaptability, and safety. The journey concludes with a recap of the key points and the significance of Auxiliary Hoists in industrial operations. Stay with us as we wrap up this exploration of the extraordinary world of Auxiliary Hoists.
Wrap it Up, Elevating Your Operations
As we conclude our exploration of the remarkable world of Auxiliary Hoists, let's take a moment to reflect on the key elements that make these lifting solutions an indispensable asset in industrial operations.
Auxiliary Hoists are more than just tools; they are efficiency boosters that redefine the way we approach lifting operations. The integration of these hoists empowers industries to handle heavier loads, streamline processes, and ultimately enhance operational efficiency. The lifting capacity is not just increased; it's optimized for precision and adaptability.
Related Products

Latest project
150 Ton Overhead Crane Installation Feedback – Paraguay Case
QDX 150 ton overhead crane in action in Paraguay. Installation photos, video, and client feedback show performance, safety, and heavy-lifting efficiency.
Free consultation to Confirm Parameters & Specifications and Get
Latest Crane Price & Crane Rate.
- Types of overhead cranes : _______?
- Optional: Overhead travelling crane, goliath gantry crane,Slewing jib crane, Single girder or double girder crane,small portable crane or kbk crane, etc.
- Capacity of overhead crane: _______?
- Optional: 0.25ton, 0.5 ton, 1 ton, 2 ton, 3ton, 5 ton, 10 ton,15ton, 20ton, 25 ton, 30ton,35ton, up to 550ton, etc.
- Crane span & lifting height : _______?
- Crane travelling length : _____?
- Control of overhead crane:_______?
- Optional: pendant/ remote/cabin control
- Voltage supply of overhead crane:_____?
- Eg,: 380V50/60HZ,3Phase or others,etc.
- Application/usage of crane:_______?
- Eg,: Steel mill, ,injection mold, cement,stone, concrete,granite, general manufacturing, etc.
Just leave a message via the contact form and our hoist and crane engineer will contact you with in 24working hours.
Get In Touch




