How 10 Ton Underhung Cranes Save Costs in Low-Headroom Facilities
How 10 Ton Underhung Cranes Save Costs in Low-Headroom Facilities
Introduction
Low-headroom facilities—like older workshops, warehouses, or factories with limited ceiling height—often face challenges when it comes to moving heavy materials efficiently. Traditional overhead cranes usually require tall building structures and reinforced supports, which can be expensive or even impossible to install in such spaces. This is where underhung bridge cranes come in. By suspending from the existing ceiling or structural beams, underhung cranes make full use of the available vertical space without the need for major construction changes.
For facility managers and engineers, cost efficiency is always top of mind. Installing a crane system isn’t just about lifting heavy loads—it’s about minimizing construction costs, reducing downtime, and keeping energy use manageable. Underhung cranes often offer a practical solution because they reduce the need for large, heavy-duty structural supports and allow for simpler installation.
The focus of this article is to show how 10-ton underhung cranes specifically provide real economic and operational advantages in low-headroom facilities. We’ll cover how they save money on construction, reduce ongoing operational costs, and still maintain the lifting capacity needed for medium to heavy industrial operations. By understanding their benefits and limitations, buyers can make smarter decisions that save money and improve workflow efficiency.
Key Points Covered in This Section:
- What underhung cranes are and why they fit low-headroom spaces
- How cost efficiency affects industrial lifting projects
- How 10-ton underhung cranes can offer both economic and operational advantages
Understanding Underhung Cranes
When it comes to cranes for low-headroom spaces, underhung cranes are often the first choice. But what exactly are they, and how do they differ from traditional overhead cranes? Let’s break it down.
Definition and Basic Design Features
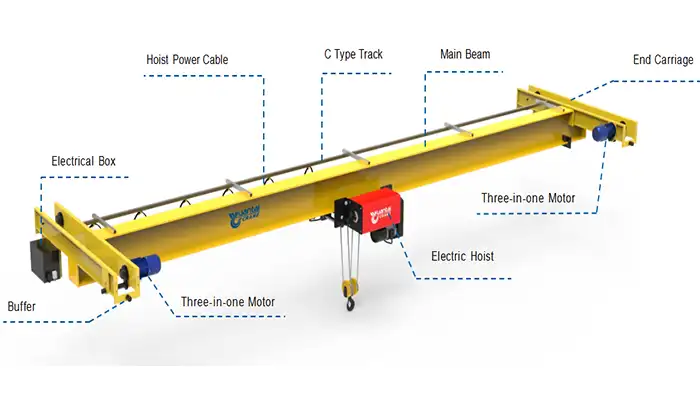
An underhung crane is a type of overhead crane that suspends from the building’s existing beams or runway structure rather than sitting on top of a gantry or bridge. This design allows the crane to operate in facilities with limited ceiling height.
Key design features include:
- Bridge girder: Runs along the top of the crane and supports the hoist trolley.
- Trolley and hoist: Moves along the bridge girder to lift and transport loads.
- End trucks: Allow the crane to move along the runway beam.
- Suspension from existing structure: Eliminates the need for extra floor-to-ceiling height.
This simple but effective design makes it ideal for workshops where every centimeter of vertical space counts.
Difference Between Underhung and Traditional Overhead Cranes
While both cranes lift heavy loads, there are clear differences:
- Installation height: Underhung cranes require less vertical space, making them suitable for low-headroom buildings.
- Support structure: Traditional overhead cranes often need reinforced beams or columns, while underhung cranes use the building’s existing structure.
- Flexibility: Underhung cranes can sometimes be relocated within the facility more easily than top-running overhead cranes.
- Cost considerations: Lower structural requirements usually mean reduced installation costs and shorter lead times.
Typical Applications in Low-Headroom Environments
Underhung cranes are widely used in industries where space is limited but lifting needs are moderate to heavy. Common applications include:
- Maintenance workshops: Moving engines, parts, or heavy equipment in repair shops.
- Warehouses: Handling pallets, coils, or other medium-heavy materials.
- Manufacturing plants: Assembly lines, small-scale steel fabrication, or plastic molding operations.
- Retrofitted facilities: Older buildings where adding extra support structures is costly or impractical.
Key Cost-Saving Advantages
Choosing the right crane can make a big difference in both upfront and ongoing costs. For low-headroom facilities, 10-ton underhung cranes provide practical advantages that go beyond just lifting heavy loads. Let’s take a closer look.
Space Optimization
Underhung cranes are designed to make the most of existing vertical space, which is critical in low-ceiling facilities. Instead of requiring tall supports or extra headroom, these cranes attach directly to structural beams.
Practical benefits include:
- Utilization of existing structural beams: No need to build additional supports or columns.
- Minimal requirement for additional floor-to-ceiling height: Ideal for older factories or retrofitted buildings.
- Flexibility in cramped or retrofitted facilities: Can navigate around machinery, mezzanines, and other overhead obstacles.
By saving space, underhung cranes allow for smoother workflows and reduce the need to rearrange equipment.
Lower Structural Investment
Installing a crane often means major construction costs. Underhung cranes reduce these expenses by relying on the existing structure rather than heavy-duty supports.
Key points:
- Reduced need for heavy-duty building support structures: The building’s beams carry the load.
- Savings on civil construction and reinforcement costs: No need for extensive concrete or steel work.
This translates into significant savings during the initial installation phase, making the project faster and more cost-effective.
Simplified Installation and Maintenance
Time is money, and underhung cranes are easier to install and maintain than many top-running alternatives.
Advantages include:
- Faster setup reduces labor costs: Less crane assembly and fewer structural modifications.
- Less complex maintenance compared to heavy double-girder cranes: Fewer moving parts exposed to wear and tear.
- Fewer downtime losses: Easier inspections and quicker repairs help keep production on track.
Facilities benefit not only from lower installation costs but also from reduced operational interruptions.
Energy Efficiency
Even at full capacity, underhung cranes generally consume less power than larger, top-running cranes.
Considerations:
- Lower power consumption for lifting and moving loads: Smaller motors and lighter bridge structures require less energy.
- Potential savings on operational energy bills: Over time, this can add up to thousands of dollars in industrial facilities.
This makes underhung cranes practical for businesses looking to control both capital and operational costs.
Adaptability and Lifecycle Cost Reduction
One of the biggest advantages of underhung cranes is their flexibility over time.
Key benefits:
- Ability to reconfigure or relocate within the facility: Supports changing workflows or production layouts without major construction.
- Long-term ROI benefits: Reduced installation, maintenance, and energy costs combine to provide a better overall return on investment.
In short, underhung cranes are not just cost-effective upfront—they continue to save money and optimize operations over the long term.
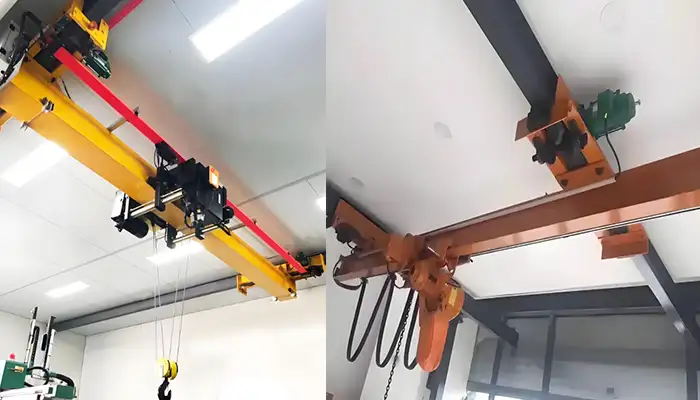

Practical Considerations for Overhead Cranes for Low-Headroom Facilities
Even though 10-ton underhung cranes offer clear cost and space advantages, proper planning is crucial to ensure safety and efficiency. Low-headroom environments present unique challenges, and a careful assessment can save headaches down the line.
Assessing Ceiling Height and Available Beam Structures
Before choosing an underhung crane, you need to understand the physical limits of your facility. Not every existing beam can safely support a 10-ton load, so a thorough inspection is essential.
Key points to consider:
- Measure ceiling-to-floor height: Ensure the crane fits without restricting headroom for other operations.
- Evaluate beam strength and spacing: Only beams with sufficient load-bearing capacity can support the crane safely.
- Check for obstacles: Pipes, lighting, and other overhead structures can interfere with crane movement.
This step ensures that the crane can operate smoothly without causing structural stress or operational hazards.
Load Requirements and Safety Factors for 10-Ton Cranes
Understanding your lifting needs is critical. A 10-ton crane should be able to handle the heaviest loads you plan to lift, plus a safety margin.
Considerations include:
- Maximum expected load: Account for single lifts and any bundled loads.
- Safety factors: Most standards recommend at least 1.25–1.5 times the maximum load for safety.
- Frequency of use: High-frequency operations may require additional maintenance planning and more robust components.
Accurate load assessment prevents overloading, reduces wear, and ensures safe operation for workers.
Integration with Existing Workflows and Production Lines
Installing a crane isn’t just about lifting—it has to fit into daily operations without creating bottlenecks or safety risks.
Practical tips:
- Plan crane travel paths: Ensure the crane moves freely without interfering with machines, storage areas, or staff.
- Coordinate with material flow: Align lifting points with production or storage locations to minimize unnecessary handling.
- Consider future changes: Allow room for possible layout adjustments or expansion of production lines.
A well-integrated crane improves productivity and reduces unnecessary handling, saving both time and costs.
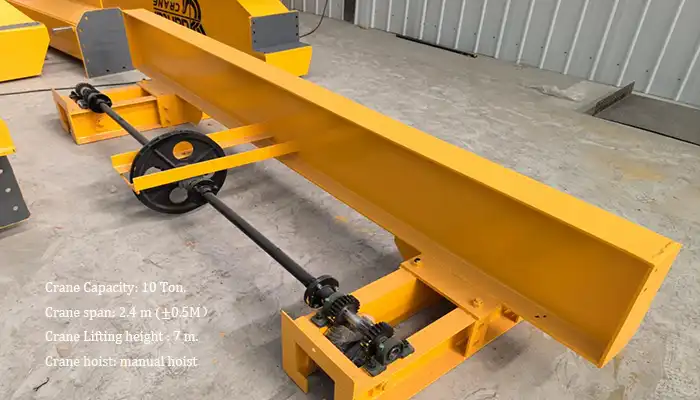

10 Ton Underhung Crane for Sale UK, Underhung Bridge Crane 10 Ton
Limitations and Mitigation Strategies
While 10-ton underhung cranes offer many advantages, it’s important to understand their limitations and plan accordingly. Recognizing these issues early can help avoid costly mistakes and ensure safe, efficient operation.
Potential Lifting Restrictions Compared to Top-Running Cranes
Underhung cranes have some operational limits:
- Span limitations: The bridge length is often constrained by the building’s beam spacing.
- Load capacity: While 10 tons is sufficient for many facilities, heavier or very frequent lifts may require a top-running solution.
- Travel speed: Underhung cranes may operate at slightly slower speeds compared to some top-running cranes.
Mitigation Tips:
- Carefully calculate maximum loads and movement distances before selection.
- Use multiple smaller lifts or dual hoists for heavier, irregular loads.
Maintenance Challenges Specific to Underhung Designs
Because underhung cranes are attached to the building structure, accessing components for maintenance can sometimes be tricky:
- Limited space around the bridge or trolley for inspection.
- Overhead beam attachments require periodic checks for structural integrity.
Mitigation Tips:
- Schedule regular inspections for both crane components and supporting beams.
- Keep maintenance pathways clear to allow safe access.
- Train staff on proper preventive maintenance routines.
Strategies to Maximize Crane Lifespan and Minimize Operational Disruptions
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for load limits, lubrication, and usage.
- Install protective covers to reduce dust, debris, or environmental damage.
- Plan workflow carefully to avoid unnecessary stops or collisions that could accelerate wear.
With proper planning and maintenance, underhung cranes can operate safely and reliably for many years.
Conclusion
10-ton underhung cranes are a practical solution for facilities with limited ceiling height. They save costs by reducing structural investment, simplifying installation, and lowering operational energy and maintenance expenses.
Key Takeaways:
- They maximize vertical space and integrate well into existing workflows.
- They reduce upfront and long-term costs while improving productivity.
- Careful planning and routine maintenance are essential for safety and longevity.
For businesses considering a low-headroom crane solution, it’s wise to consult experienced crane manufacturers. Their expertise ensures the right crane is selected, installed correctly, and maintained efficiently.
In short, underhung cranes offer a cost-effective, space-saving, and operationally practical choice for low-headroom industrial facilities.
Related: How Underhung Bridge Cranes Handle Loads Near Workshop Walls